前言
Masonry是一个轻量级的布局框架 拥有自己的描述语法 采用更优雅的链式语法封装自动布局 简洁明了 并具有高可读性 而且同时支持 iOS 和 Max OS X。
官方的介绍其实是非常详细的了,可以移步到其Masonry-Github下载官方源码Demo,我也非常推荐看官方的介绍。
介绍
使用过官方的NSLayoutConstraints的话,应该会很清楚它过于繁琐和麻烦,而使用Masonry,它遵循链式编程思想,其结构简单,使用方便,就像他的简介一样。
首先我们来看下官方的Autolayout代码
1 | UIView *superview = self; |
看见这样的约束,是不是感到头大,很简单的事件,却变得繁琐起来,对于开发来说,完全是得不偿失的事情,如此还不如用CGRectMake来的省心。
而使用Masonry,看以下代码
1 | UIEdgeInsets padding = UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 10, 10, 10); |
甚至更短
1 | [view1 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) { |
.equalTo相当于NSLayoutRelationEqual
.lessThanOrEqualTo相当于NSLayoutRelationLessThanOrEqual
.greaterThanOrEqualTo相当于NSLayoutRelationGreaterThanOrEqual
安装
普遍的两种安装方法:
1.直接进入github进行源码下载 引入头文件
#import "Masonry.h"2.使用CocoaPod进行下载
pod 'Masonry'
使用
Masonry支持的属性
1 | @property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *left; |
这些属性与NSLayoutAttrubute的对照表如下
| Masonry | NSAutoLayout | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| left | NSLayoutAttributeLeft | 左侧 |
| top | NSLayoutAttributeTop | 上侧 |
| right | NSLayoutAttributeRight | 右侧 |
| bottom | NSLayoutAttributeBottom | 下侧 |
| leading | NSLayoutAttributeLeading | 首部 |
| trailing | NSLayoutAttributeTrailing | 尾部 |
| width | NSLayoutAttributeWidth | 宽 |
| height | NSLayoutAttributeHeight | 高 |
| centerX | NSLayoutAttributeCenterX | 横向中点 |
| centerY | NSLayoutAttributeCenterY | 纵向中点 |
| baseline | NSLayoutAttributeBaseline | 文本基线 |
在使用Masonry的时候,我们不需要在手写 self.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = NO;,点进Masonry头文件,查看起方法,我们可以看到他每个方法里面都帮我们加上了这句话。
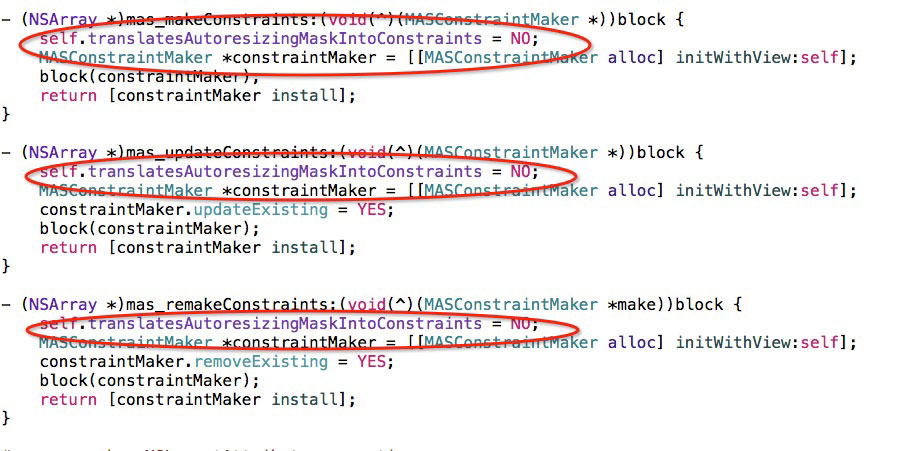
另外需要注意的是在xib或者storyboard中使用masonry框架相关方法的时候要将use Auto layout选项去掉,否则会不起作用。
1.显示一个View
我们创建一个项目, 在其中间放上一个尺寸100*100,父视图居中的View
1 | UIView * blueView= [UIView new]; |
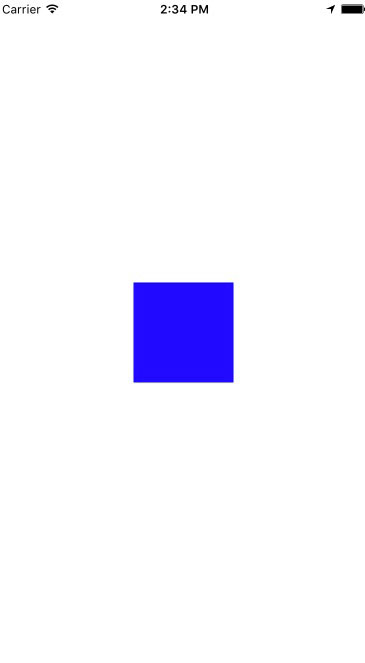
我们来每行逐一讲解以下,
-首先注意一点,在我们使用masonry约束的时候,一定要先将view先添加到superview上 否则会报错。
[self.view addSubview:blueView];-
[blueView mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) { }];这是一个Block块,mas_makeConstraints就是Masonry的autolayout添加函数 将所需的约束添加到block中即可。
make.width.equalTo(@100);约束其宽度为100,make.height.mas_equalTo(100);约束其高度为100,
make.center.equalTo (self.view);设置对self.view居中。
对于以上几个地方,我们来简单说下,
首先在Masonry中能够添加autolayout约束有三个函数
1 | //mas_makeConstraints 只负责新增约束 Autolayout不能同时存在两条针对于同一对象的约束 否则会报错 |
1 | //mas_updateConstraints 针对上面的情况 会更新在block中出现的约束 不会导致出现两个相同约束的情况 |
1 | //mas_remakeConstraints 则会清除之前的所有约束 仅保留最新的约束 |
在我们清楚了这几个函数的使用条件后,便可轻松应对
在上面代码中 make.width.equalTo(@100);和make.height.mas_equalTo(100);都是约束代码,但一个使用的是equalTo另一个是mas_equalTo,同样的效果,那他们的区别在哪里呢?其实mas_equalTo是一个MACRO,比较的是值,直接填写数字即可,equalTo比较的是view,是个对象,需要将里面的东西添加@转成ID类型,当然我们也可以用 make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(100, 100));来直接设置宽高,make我们则看做当前对象,就像self一样。
2.让View的高度是宽度的一倍
还是刚才的代码, 我们在上面添加约束,
1 | UIView * blueView= [UIView new]; |
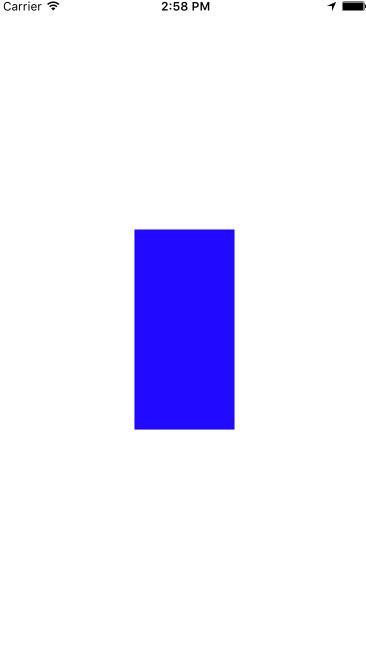
我们可以看到在约束中,我们可以直接使用multipliedBy函数,并设置offset。
如果我们将offset设置为100,也就是宽的大小make.height.equalTo(blueView.mas_width).multipliedBy(2.f).offset(100.f);
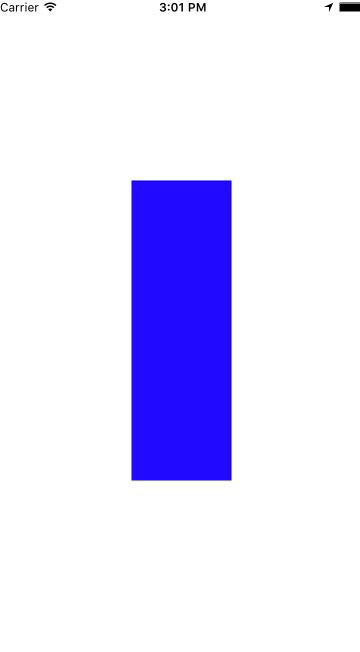
用链式语法去读它,你可以这样读,它的高度是它宽度的2倍加上100.
我们不光可以对其宽高设置,也可以对它的center,edges,size等,同时也可以设置它的优先级
1 | make.edges.equalTo(self.view).insets(UIEdgeInsetsMake(50, 50, 50, 50)); |
1 | make.size.equalTo(self.view).sizeOffset(CGSizeMake(-100, -100)); |
1 | make.center.equalTo(self.view).priority(MASLayoutPriorityFittingSizeLevel); |
我应该在哪里使用约束?
对于这个问题,直接看官方给的以下代码
1 | @implementation DIYCustomView |
结尾
Masonry是一款非常好用的第三方约束, 本文只是简单介绍了它的使用, 相信你对它也有了一定的了解,它的出现对一些喜欢纯代码的童鞋给予了极大的便利,比如我。。,需要更多的了解它,最好去看他的Github,下载他的示例Demo,你会发现他更强大的地方。 当然你也可以继续关注本blog,我会在以后更深入的讲解它的使用。